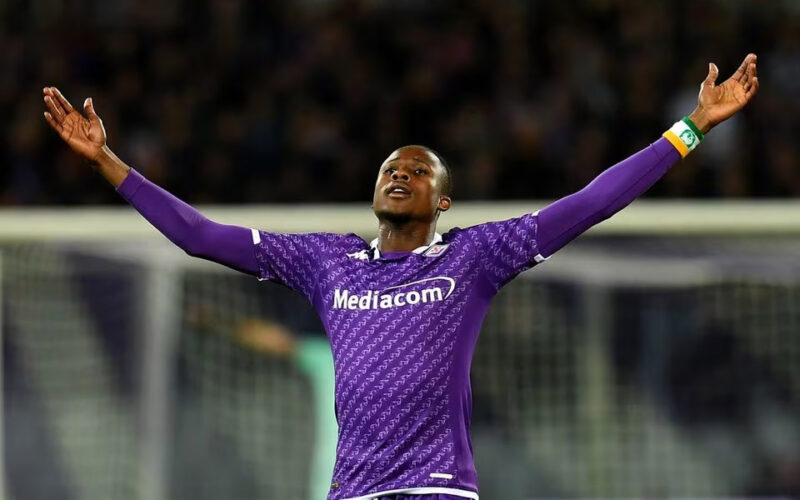
Fiorentina’s Kouame treated for malaria
FIORENTINA winger Christian Kouame has been treated in hospital for malaria, the Italian Serie A club said. The 26-year-old was in the Ivory Coast squad that won the recent Africa Cup of Nations and played in the quarter-finals. "Christian has gone into hospital to receive treatment and will continue to be assessed over the coming days," Fiorentina said in a statement. Fiorentina are seventh in Serie A with 38 points. Kouame has played 22 matches for them this season, scoring one goal and providing one assist.