Children most at risk as measles cases soar from Ethiopia to Yemen
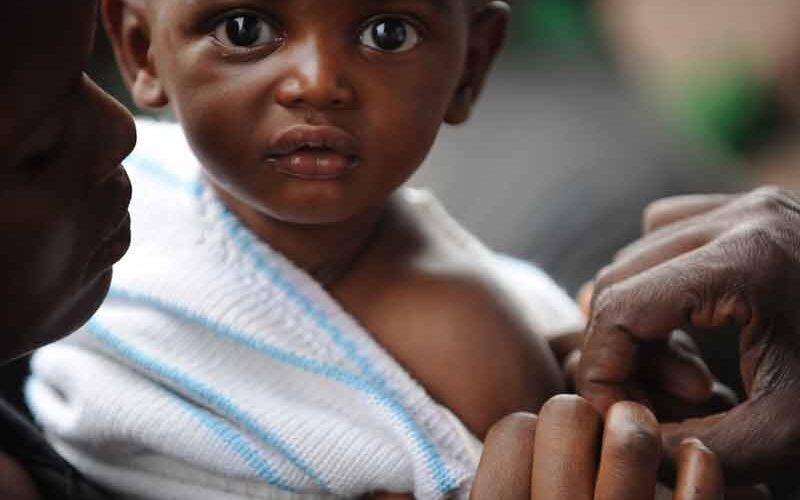
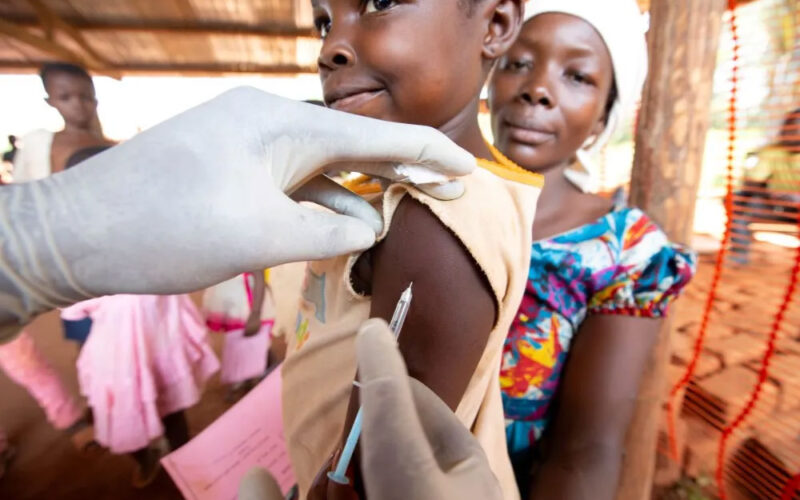
The urgency of Abdirizak Ahmed's efforts to fight a measles outbreak in Ethiopia hit home last month when two of the aid worker's colleagues lost children to the disease, which is making a comeback from Africa to India and Britain. "Both boys died before they reached the 13th month or 14th month of life ... It's devastating," said Abdirizak, who works for charity Save the Children in the Horn of Africa country, which reported 10,000 cases in 2023 - the world's highest toll after Yemen, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and India, according to World Health Organization (WHO) data. COVID-19 disrupted routine vaccinations against measles globally in…