THOMAS PETER and ALESSANDRO DIVIGGIANO
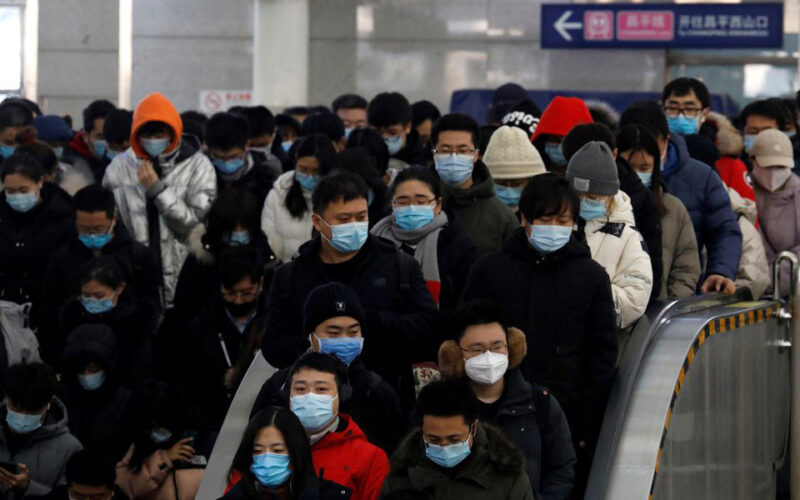
DOZENS of hearses queued outside a Beijing crematorium, even as China reported no new COVID-19 deaths in its growing outbreak, sparking criticism of its virus accounting as the capital braces for a surge of cases.
After widespread protests, the country of 1.4 billion people this month began dismantling its unpopular “zero-COVID” lockdown and testing regime, which largely kept the virus under control for three years though at a great economic and psychological cost.
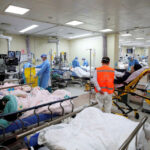
The abrupt change caught a fragile health system unprepared, with hospitals scrambling for beds and blood, pharmacies for drugs and authorities racing to build special clinics. Experts say China could face more than a million COVID deaths next year.
The head of the World Health Organization said it is concerned about the spike in infections and is supporting the government to focus on vaccinating those at the highest risk.
Amid a heavy police presence outside a crematorium in Beijing’s Tongzhou district, a Reuters witness saw about 40 hearses queuing to enter while the parking lot was full.
Inside, family and friends, many wearing traditional white clothing and headbands of mourning, gathered around about 20 coffins awaiting cremation. Staff wore hazmat suits and smoke rose from five of the 15 furnaces.
Reuters could not verify whether the deaths were caused by COVID.
Some Beijing residents have to wait days to cremate relatives or pay steep fees to secure faster service, funeral home workers said.
A worker at one Beijing funeral parlour posted on social media an offer of “speedy arrangement of hearses, no queue for cremation” for a fee of 26,000 yuan ($3,730).
Reuters could not verify the offer.
‘2020 MINDSET’
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus told reporters the agency needed more detailed information on disease severity, hospital admissions and requirements for intensive care units for a comprehensive assessment.
“The WHO is very concerned over the evolving situation in China, with increasing reports of severe disease,” he said.
His comment came as the German government confirmed it has sent its first batch of BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines to China to be administered initially to German expatriates.
China has nine domestically developed COVID vaccines approved for use. But none has been updated to target the highly infectious Omicron variant, as Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna have for boosters in many countries.
China uses a narrow definition of COVID deaths and reported no new fatalities for Tuesday, even crossing one of its overall tally since the pandemic began, now at 5,241 – a fraction of the tolls of many much less populous countries.
The National Health Commission said on Tuesday only deaths caused by pneumonia and respiratory failure in patients who had the virus are classified as COVID deaths.
Benjamin Mazer, an assistant professor of pathology at Johns Hopkins University, said that classification would miss “a lot of cases”, especially as people who are vaccinated, including those with Chinese shots, are less likely to die of pneumonia.
Blood clots, heart problems and sepsis – an extreme body response to infection – have caused countless deaths among COVID patients around the world.
“It doesn’t make sense to apply this sort of March 2020 mindset where it’s only COVID pneumonia that can kill you,” Mazer said.
“There’s all sorts of medical complications.”
‘ACT QUICKLY’
The death toll might rise sharply, with the state-run Global Times newspaper citing a Chinese respiratory expert predicting a spike in severe cases in Beijing over the coming weeks.
“We must act quickly and prepare fever clinics, emergency and severe treatment resources,” Wang Guangfa, a respiratory specialist from Peking University First Hospital, told the newspaper.
Wang expected the COVID wave to peak in late January, with life likely to return to normal by late February or early March.
The NHC also played down international concern about the possibility of virus mutations, saying the likelihood of new strains that are more pathogenic was low.
Paul Tambyah, President of the Asia Pacific Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infection, supported that view.
“I do not think that this is a threat to the world,” he said. “The chances are that the virus will behave like every other human virus and adapt to the environment in which it circulates by becoming more transmissible and less virulent.”
Several prominent scientists and WHO advisers told Reuters a potentially devastating wave to come in China means it may be too early to declare the end of the global pandemic emergency.
SICK WORKERS
Some U.S. and European officials have offered to help mitigate a crisis they fear will hurt the global economy and disrupt supply chains.
From the epicentre in northern China, infections are spreading to manufacturing belts, including the Yangtze River Delta, near Shanghai, disrupting workforces.
Retail and financial service businesses have been hard hit by staff shortages, with factories not far behind, industry bodies say.
Staff at Communist Party and government institutions or enterprises in the southwestern city of Chongqing who have mild COVID symptoms can go to work if they wear a mask, the state-run China Daily reported.
Other media reported similar decisions in other cities.
China is still largely cut off from the outside world, but there are signs COVID restrictions on international travel are easing too.
Chelsea Xiang, 35, said she only needed to do two days of quarantine in the southwestern city of Chengdu after returning from Hong Kong on Sunday, rather than the officially required minimum of five.
“I feel I have my human rights again,” Xiang said.