SONIA ELKS
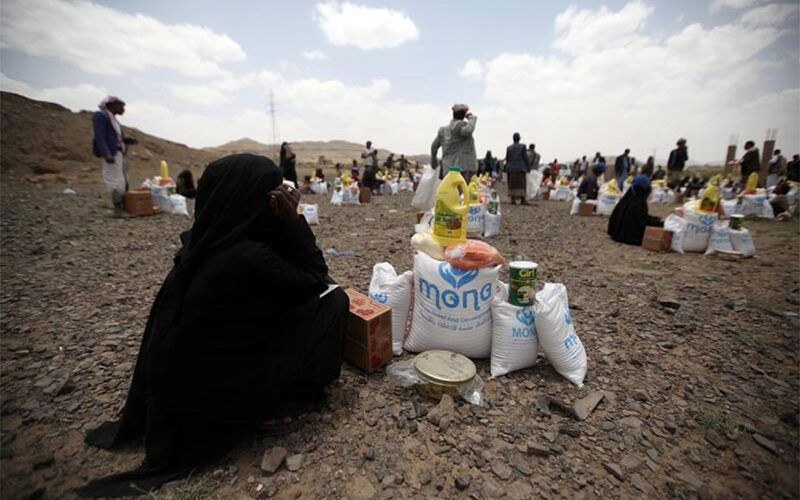
WITH millions on the brink of famine in four nations, women and girls will be hardest hit due to cultural beliefs and COVID-19’s economic impacts, according to the charity CARE.
The coronavirus pandemic could nearly double the number of acutely food insecure people to more than 270 million by the end of 2020, the United Nations said this week, with famine looming in parts of Yemen, South Sudan, Burkina Faso and Nigeria.
“There is a huge risk that millions of women and girls around the world are already going hungry,” Sarah Fuhrman, a humanitarian policy specialist with CARE, told the Thomson Reuters Foundation.
“Everything we know about food security and who goes hungry indicates that women and girls are always at a particular risk for being the ones to eat last and the ones to eat least.”
The coronavirus pandemic has wreaked havoc on economies worldwide, leading the World Bank last month to predict a rise in extreme poverty for the first time in 20 years, as millions also grapple with the impacts of climate change and conflict.
One in nine people do not have enough to eat, reversing decades of progress in reducing world hunger, according to the World Food Programme, which won the Nobel Peace Prize this year for its efforts to stop hunger being used as a weapon of war.
Women and girls are facing a double burden amid the COVID-19 pandemic, said CARE, with women’s disproportionate job losses meaning many struggles to provide for their households, while social norms often dictate they should feed men and boys first.
The United Nations on Tuesday said it would release $80 million to tackle hunger in Afghanistan, Burkina Faso, Democratic Republic of Congo, Nigeria, South Sudan and Yemen, and another $20 million for drought-afflicted Ethiopia.
“No one should view a slide into famine as an inevitable side effect of this pandemic,” said the U.N. humanitarian chief Mark Lowcock in a statement.
“The prospect of a return to a world in which famines are commonplace would be heart wrenching and obscene in a world where there is more than enough food for everyone.”
CARE called for more funding to tackle COVID-19’s impacts, as well as specific efforts to protect women and girls by ensuring they are involved in decision-making and programmes target their needs.
“If we don’t have women and girls involved in telling us what’s wrong and how to fix it, we are never going to get it right,” said Fuhrman. – Thomson Reuters Foundation.